Unleash the power of SQL with this step-by-step guide on transitioning your Excel data seamlessly. Say goodbye to spreadsheet chaos!
Table of Contents
Welcome, teachers turned data analysts! If you’re ready to take your data management skills to the next level by transitioning from Excel to SQL, you’re in the right place. In this post, we’ll guide you through the process step-by-step to ensure a smooth transition. Let’s dive in!
Understanding the Basics of SQL
SQL, or Structured Query Language, is a powerful tool for managing and manipulating data in databases. It allows you to organize and retrieve data efficiently, making it a popular choice for data analysts and professionals. At its core, SQL is all about working with tables, running queries, and using commands to interact with your data.
As you venture into the world of SQL, it’s essential to grasp these fundamental concepts to navigate databases successfully. Think of SQL as your key to unlocking the potential of your data in a structured and effective way.
Benefits of Using SQL over Excel
While Excel has been a reliable tool for many professionals, SQL offers several advantages when it comes to handling large and complex datasets. SQL databases are known for their scalability, performance, and robust data integrity features, ensuring that your data stays secure and consistent.
By transitioning from Excel to SQL, you’ll not only streamline your data management processes but also unlock new possibilities for analyzing and visualizing your data. Say goodbye to Excel’s limitations and hello to the expansive world of SQL databases!
Importing Data from Excel to SQL
One of the first steps in transitioning from Excel to SQL is importing your existing data into a SQL database. While this may seem daunting at first, fear not—We’ve got you covered. Below are some simple steps to seamlessly transfer your Excel data into SQL:
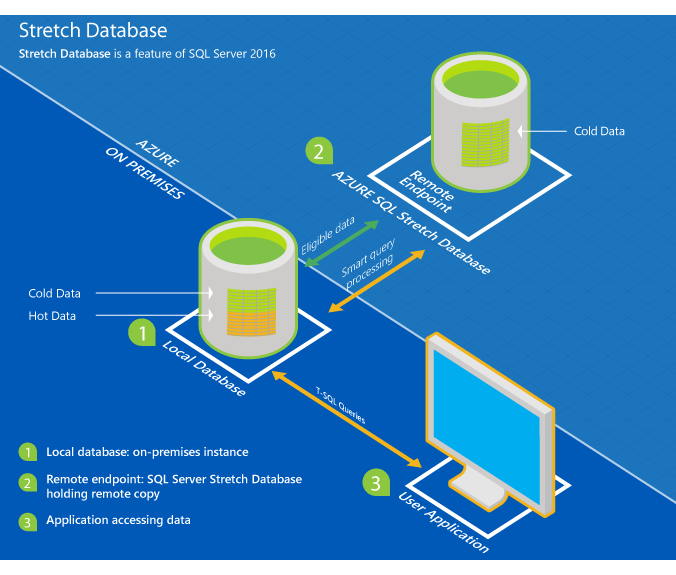
Image courtesy of learn.microsoft.com via Google Images
To begin the process, export your Excel data into a CSV file to facilitate importing it into SQL. Next, open your SQL database, choose the import option, and select the CSV file containing your data. Follow the on-screen instructions to map the columns from your CSV file to the appropriate fields in the SQL database. Once completed, voila! Your Excel data is now safely stored in a SQL database, ready for further analysis and manipulation.
Structuring Data in SQL
Organizing your data effectively is crucial in SQL for optimal performance and data management. Two key concepts to understand are normalization and data modeling. Normalization involves breaking down data into smaller, more manageable tables, reducing redundancy and improving data integrity. Data modeling, on the other hand, focuses on designing tables and defining relationships between them, ensuring a cohesive structure for your database.
By implementing these best practices, you’ll create a solid foundation for storing and retrieving data, making your SQL database a robust and efficient tool for your data analysis tasks.
Writing SQL Queries
Writing SQL queries is where the magic happens. Whether you’re retrieving specific data, performing calculations, or filtering results, mastering the art of SQL queries is key to unlocking the full potential of your data. Let’s start with the basics.
Image courtesy of www.astera.com via Google Images
To write a basic SELECT query, simply specify the columns you want to retrieve from a table. For example, to fetch all student names from a ‘Students’ table, you would write: SELECT name FROM Students; Experiment with different SELECT queries to familiarize yourself with the syntax and capabilities of SQL.
Advanced SQL Techniques
Once you’re comfortable with basic queries, it’s time to explore more advanced SQL techniques to enhance your data analysis skills. JOINs are powerful tools that allow you to combine data from multiple tables based on specified criteria. By mastering JOINs, you can retrieve complex datasets that provide deeper insights into your data.
Additionally, aggregating data using GROUP BY and HAVING clauses enables you to summarize and analyze data efficiently. These advanced techniques are essential for performing complex calculations and generating valuable insights from your SQL database.
Data Manipulation in SQL
Manipulating data in SQL involves using commands like INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE to add, modify, or remove data from your database. These commands allow you to make changes to your dataset, ensuring that your data remains up-to-date and accurate.
Image courtesy of www.quora.com via Google Images
For instance, you can use the INSERT command to add new records to a table, the UPDATE command to modify existing data, and the DELETE command to remove unwanted records. By mastering data manipulation commands, you’ll have full control over your data in the SQL database.
Data Visualization with SQL
Visualizing data is an essential part of data analysis, enabling you to communicate insights effectively. SQL offers several tools and techniques for visualizing data within the database itself. By leveraging SQL’s reporting and dashboard features, you can create dynamic visualizations that enhance your data analysis workflows.
Whether you’re generating reports, charts, or graphs, SQL provides a range of options for visualizing your data in a meaningful way. Explore these visualization capabilities to elevate the presentation of your analysis results.
Tips for Transitioning to SQL Successfully
As you embark on your journey from Excel to SQL, keep in mind some key tips to ensure a successful transition:

Image courtesy of powerusers.microsoft.com via Google Images
Avoid common pitfalls like data duplication and inconsistent data formats by following data normalization practices. Stay organized and document your SQL queries to track your analysis process effectively. Lastly, don’t hesitate to seek additional resources and training to improve your SQL skills continuously.
By incorporating these tips into your transition to SQL, you’ll navigate the process smoothly and maximize the potential of your data management capabilities.
Conclusion
Congratulations, teachers turned data analysts, on taking the leap from Excel to SQL! By understanding the basics, leveraging the benefits, and mastering the techniques discussed in this post, you’re well on your way to unlocking the full potential of your data management skills with SQL.
Remember, transitioning to SQL is a journey filled with learning opportunities and growth. Embrace the process, experiment with SQL queries, and explore the endless possibilities that SQL databases offer for your data analysis tasks.
Stay curious, stay determined, and let SQL be your guide to transforming your data management practices for the better. Exciting times await in the world of SQL—Are you ready to excel in your data journey?
Generated by Texta.ai Blog Automation

