Uncover the secrets to effortlessly transforming Excel data into a powerful SQL database with our step-by-step guide.

Image courtesy of Pok Rie via Pexels
Table of Contents
Hey there, teachers turned data analysts! Are you ready to take your data analysis skills to the next level by transitioning from Excel to SQL? SQL (Structured Query Language) is a powerful tool for managing and analyzing large datasets, and once you start using it, you’ll wonder how you ever managed without it. In this blog post, we’ll cover all the essentials you need to know to make a smooth transition from Excel to SQL. Let’s dive in!
Understanding the Basics of SQL
If you’re used to working with spreadsheets in Excel, moving to SQL can feel like a big change. SQL is a specialized programming language used for managing and manipulating structured data. Unlike Excel, which is more manual and formula-based, SQL allows you to write queries to extract, analyze, and transform data. This shift offers numerous benefits, including improved data accuracy, scalability, and efficiency in data analysis tasks.
Installing and Setting Up SQL Software
Before you can start working with SQL, you’ll need to install SQL software on your computer. There are various options available, including MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server. Each has its strengths and weaknesses, so it’s essential to choose the one that best suits your needs. Installing SQL software is typically straightforward – just follow the installation instructions provided by the software vendor. Once installed, you’ll need to set up a database to work with, which acts as a central repository for your data.
Learning SQL Syntax
One of the key aspects of transitioning to SQL is understanding the syntax of the language. SQL uses a set of commands to interact with databases, such as SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE. Learning these basic commands is essential for writing queries to retrieve and manipulate data. There are plenty of online resources available to help you learn SQL syntax, including tutorials, courses, and documentation.
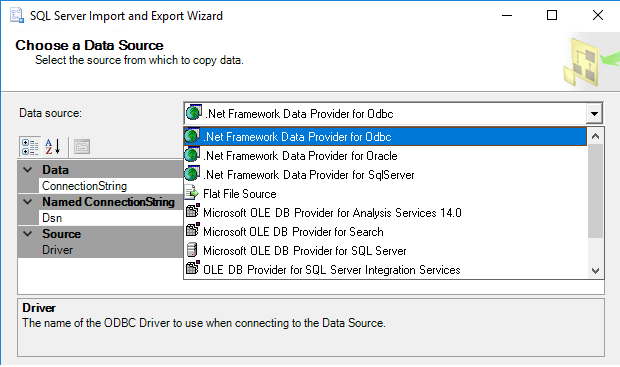
Image courtesy of www.sqlshack.com via Google Images
Importing Data from Excel to SQL
Once you’re comfortable with the basics of SQL, the next step is to import your data from Excel into your SQL database. There are several methods you can use to accomplish this, such as using CSV files, ODBC connections, or specialized import tools. It’s crucial to ensure the accuracy of the data during the import process, as small errors can lead to significant issues later on. Be sure to double-check your data and validate it after importing to ensure everything has been transferred correctly.
Manipulating Data in SQL
With your data imported into SQL, you can start manipulating it to extract valuable insights. SQL provides powerful tools for filtering, sorting, and aggregating data, making it easy to perform complex analyses. You can use functions like COUNT, SUM, AVG, and GROUP BY to summarize data and gain a deeper understanding of your dataset. Additionally, you can join tables to combine data from multiple sources, enabling you to perform more advanced analyses.
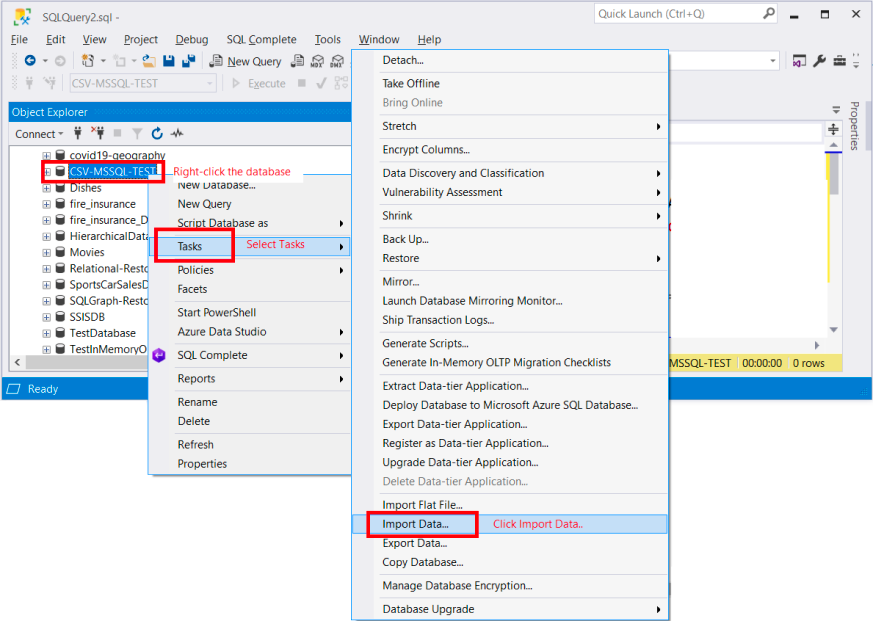
Image courtesy of blog.devart.com via Google Images
Creating Reports and Visualizations in SQL
SQL isn’t just about querying data – you can also use it to generate reports and visualizations. There are several tools and techniques for creating reports in SQL, such as using the SELECT statement to retrieve specific data or the PIVOT function to pivot data into a more readable format. You can also create charts and graphs directly in SQL to visualize trends and patterns in your data. These reports and visualizations can be exported to share with colleagues or stakeholders.
Best Practices for SQL Query Writing
As you start writing more complex SQL queries, it’s essential to follow best practices to ensure your code is efficient and maintainable. This includes writing clear and concise queries, using comments to document your code, and organizing your queries logically. Avoiding common mistakes, such as using ambiguous column names or unnecessary joins, will help streamline your queries and improve their performance.
Image courtesy of sqlspreads.com via Google Images
Advanced SQL Techniques
Once you’re comfortable with the basics of SQL, you can explore more advanced techniques to enhance your data analysis skills. This includes using subqueries and nested queries to perform complex data manipulations, working with date and time data using date functions, and utilizing advanced SQL functions like CASE statements and window functions. These techniques allow you to tackle more challenging data analysis tasks and extract deeper insights from your datasets.
Practice, Practice, Practice
Like any new skill, mastering SQL takes practice. The more you work with SQL, the more comfortable and proficient you’ll become. Look for datasets to practice with online, participate in SQL challenges or competitions, and continue learning new SQL techniques. By regularly practicing and honing your SQL skills, you’ll become a confident and skilled data analyst in no time.

Image courtesy of www.sqlshack.com via Google Images
Conclusion
Congratulations on taking the first steps in transitioning from Excel to SQL! With the right guidance and practice, you’ll soon be proficient in using SQL for data analysis tasks. Remember to start with the basics, explore different SQL techniques, and continue practicing to improve your skills. By making the switch from Excel to SQL, you’ll unlock new possibilities for analyzing data and gaining insights that can have a significant impact on your work as a teacher turned data analyst.
Generated by Texta.ai Blog Automation